Economic indicators measure a country’s economic strength. They can be related to a specific segment of the economy (for example, retail or housing) or the overall economy (for example, unemployment or GDP).
These measurements are of great interest to traders, as they affect currency prices.
Next, you will learn about two of the most important economic indicators affecting currency price – inflation and interest rates.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are one of the main factors of price changes in the Forex market. A country’s base interest rate is determined by the Central Bank of the respective country. The Central Bank uses these rates as a tool to manage the economy. It raises interest rates to curb inflation or lowers them to stimulate growth.
Changes in interest rates affect borrowers
The entire mechanism using interest rates as a tool is as follows:
Central banks of countries lend money to some banks, the price of the loan for such banks is the central base interest rate. Then banks lend money in the form of loans to other banks and consumers. These loans require interest payments. The minimum interest rate in this case equals the base rate.
If the Central Bank raises the base interest rate, borrowers will have to pay more for borrowed money. This will reduce the amount of money left for spending and other needs, which also affects the economy.
Example using a mortgage
For example, if the interest rate rises, those who took out a mortgage will see an increase in monthly payments.
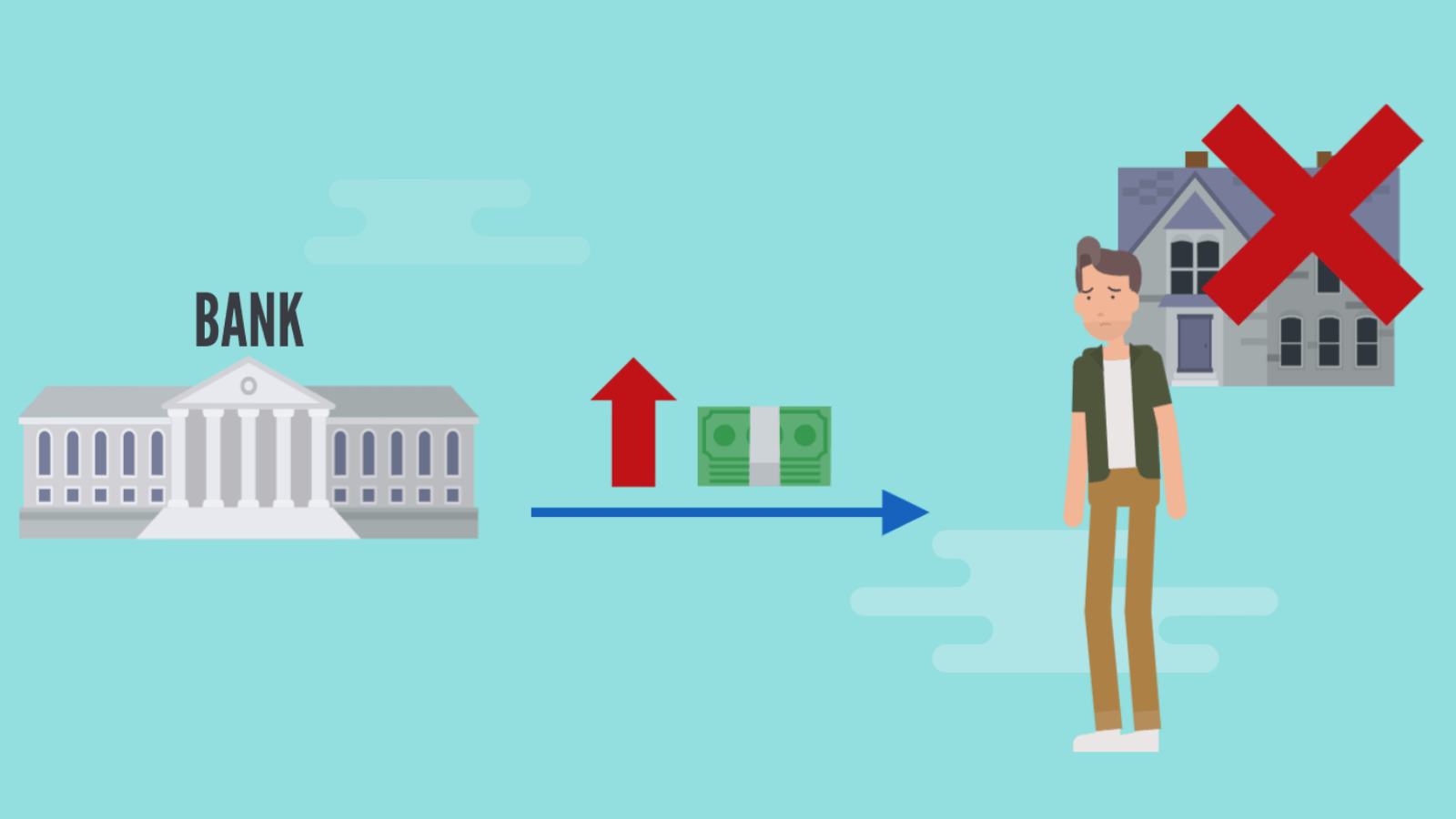
Thus, an increase in interest rates leads to curbing economic problems (for example, inflation), as a larger sum has to be paid for the monthly mortgage. And there isn’t as much money left for spending on other services or goods.
However, if the Central Bank is concerned about low economic growth, then lowering interest rates will reduce mortgage payments. Then people may have extra money to spend each month. This will stimulate the economy.
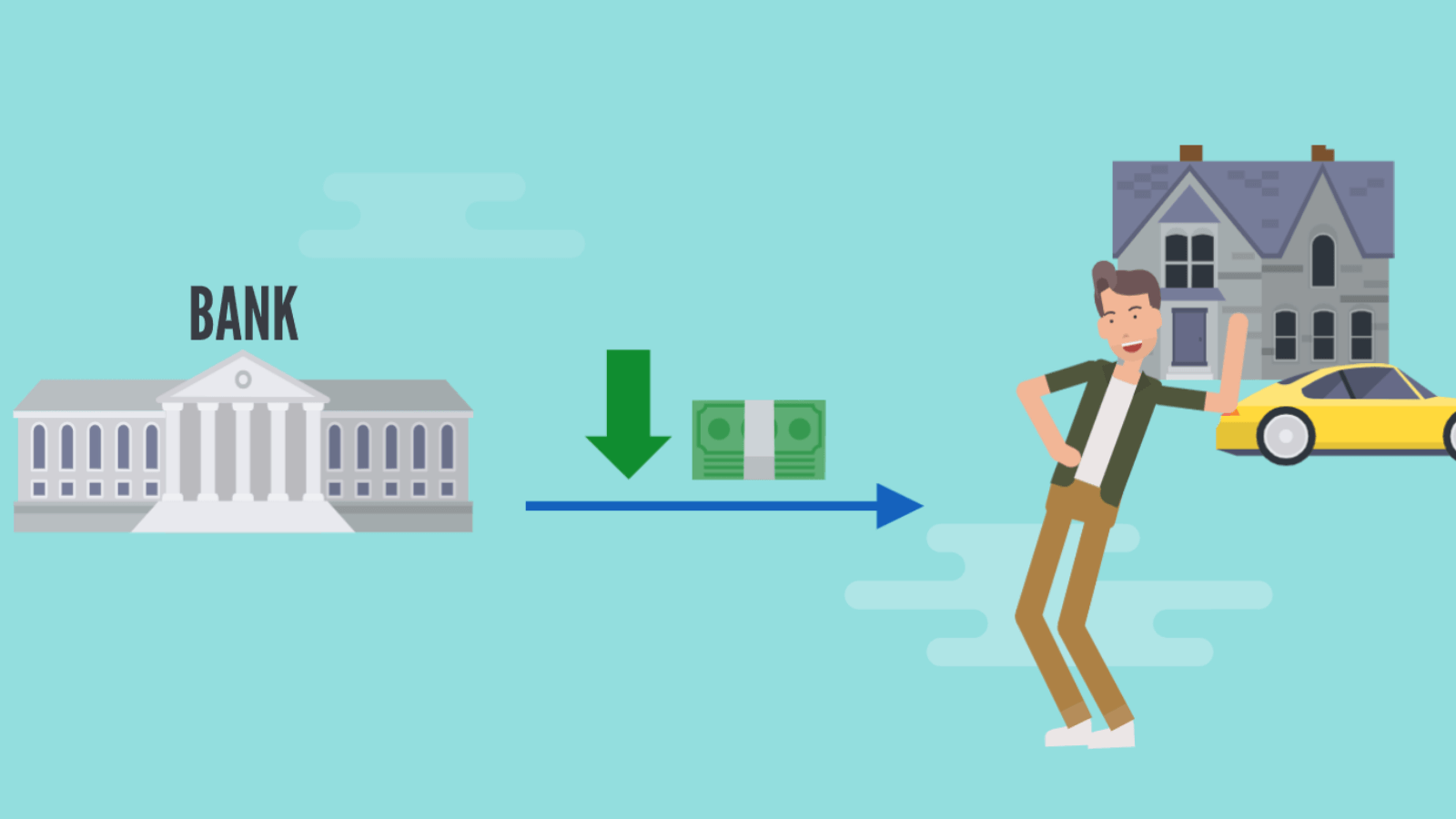
This use of interest rates applies not only to mortgage payments. Companies that borrow for growth, invest, or hire workers are also subject to the influence of these loans. If companies have to pay a larger sum because interest rates have risen, this will limit the funds available for investment.
The Impact of Interest Rates on Currency
Largely, high interest rates are an indicator of a strong economy. And investors are more likely to invest money in a growing economy. Therefore, the demand for the local currency increases, and so does its value.
Higher interest rates also mean greater profit from the capital that you hold in bank accounts. Investors often invest in countries with high interest rates, as they get a larger profit for storing their money there.
Therefore, higher interest rates will increase demand for a country’s currency, and consequently, its price will rise under normal economic conditions.
Inflation
Inflation measures the rate of cost increase for goods or services over a certain time. An elevated level of inflation will mean prices will rise faster. Meanwhile, if the level of inflation decreases, the cost of services and goods will still rise but at a slower rate.
If the level of inflation rises, people will spend their incomes faster. This can have a negative impact on the economy and the currency.
But if there is deflation in a country (prices are falling), investors may see this as a sign of economic weakness. Therefore, deflation can also negatively impact the currency price.
Central Banks often strive for a certain level of inflation
Therefore, the Central Bank aims for a permissible inflation level. For example, it can be 2-3 percent.
If the inflation level is within this range, the currency will not react significantly to it. The currency price changes on a larger scale if inflation falls outside this range.
To protect consumers from excessive inflation, Central Banks try to raise interest rates. This reduces consumers’ purchasing power, and the cost of services and goods will decrease due to lower demand. When demand decreases, the cost falls or stops rising.
When inflation data turns out to be higher than expected, traders might buy the currency in advance of the expected interest rate increase from the Central Bank. This can lead to an increase in the currency price. But the opposite can also occur, as excessive inflation can lower the value of capital in the economy. This will cause the currency price to fall. This makes the inflation level complicated to use when a trader determines the likelihood of a currency price falling or rising using this economic indicator.
Hawkish vs. Dovish
The terms “dovish” and “hawkish” are associated with a Central Bank’s stance on maintaining the balance between growth and inflation.
If a Central Bank focuses on inflation, it is considered hawkish and is likely to set high interest rates. Conversely, if the Central Bank is more concerned about growth, it is deemed dovish and is likely to set lower interest rates.