To trade on financial markets, you will need a broker. But who is this? Let’s consider an example for a better understanding.
Suppose you need to buy peaches. For this, you will go to the nearest market. The peach will be the item you want to buy, and the market will be the place of purchase, as all traders sell there.
On the other hand, sellers need buyers. Where are most buyers? That’s right – also in the market.
So it turns out that the market is a meeting place for both sides of trade. At the same time, no one hands over the peaches directly, the sellers first lay them out on their counters.
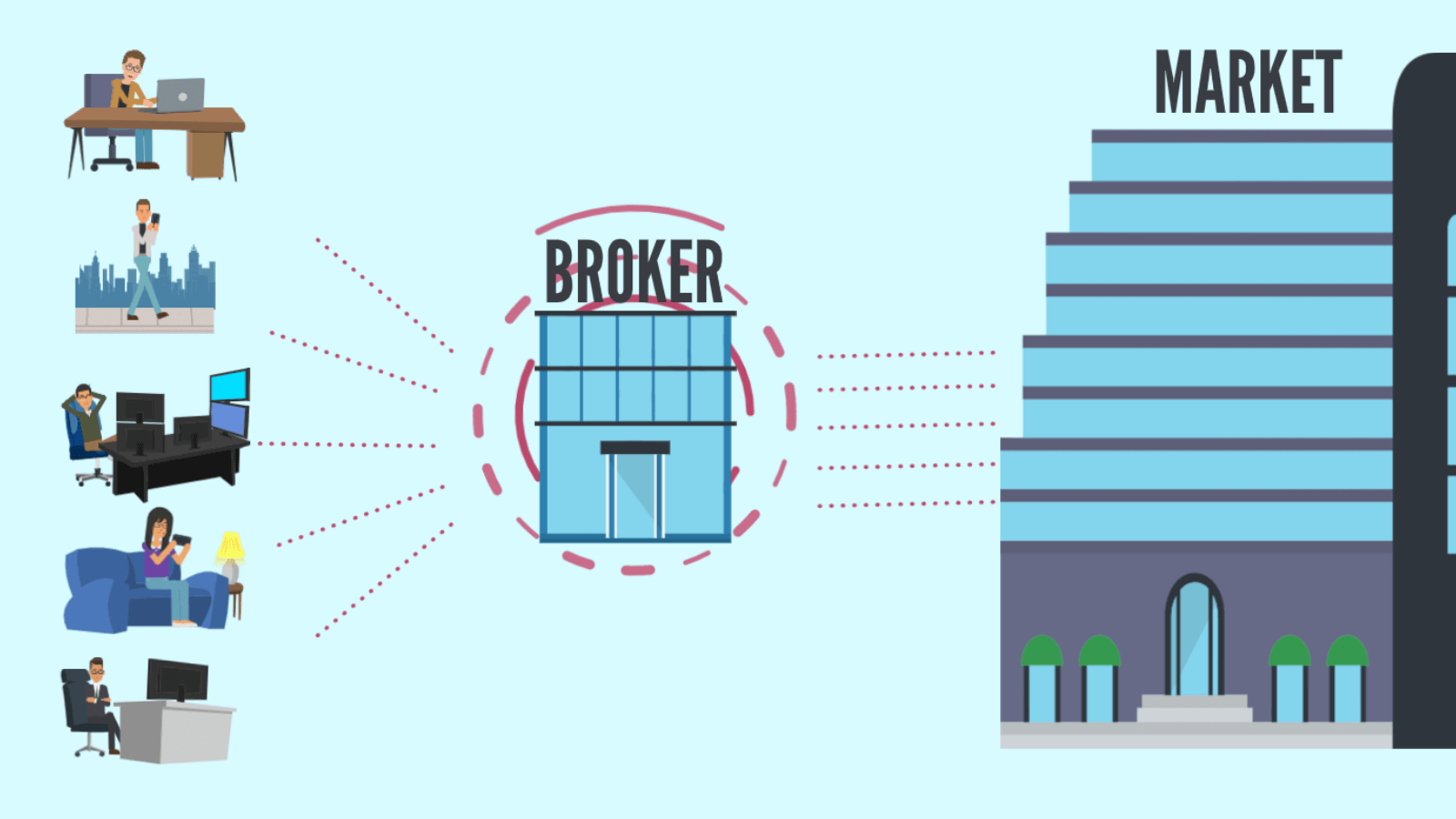
Everything happens the same way on financial markets. Sellers and buyers there work with financial instruments. Therefore, a place is needed where they could meet and sell (buy) the instrument. And also a means for trading is required.
On the financial market, the seller and the buyer can live very far apart from each other. For the seller to find buyers, some system is needed. This is where the broker comes in.
Financial Broker
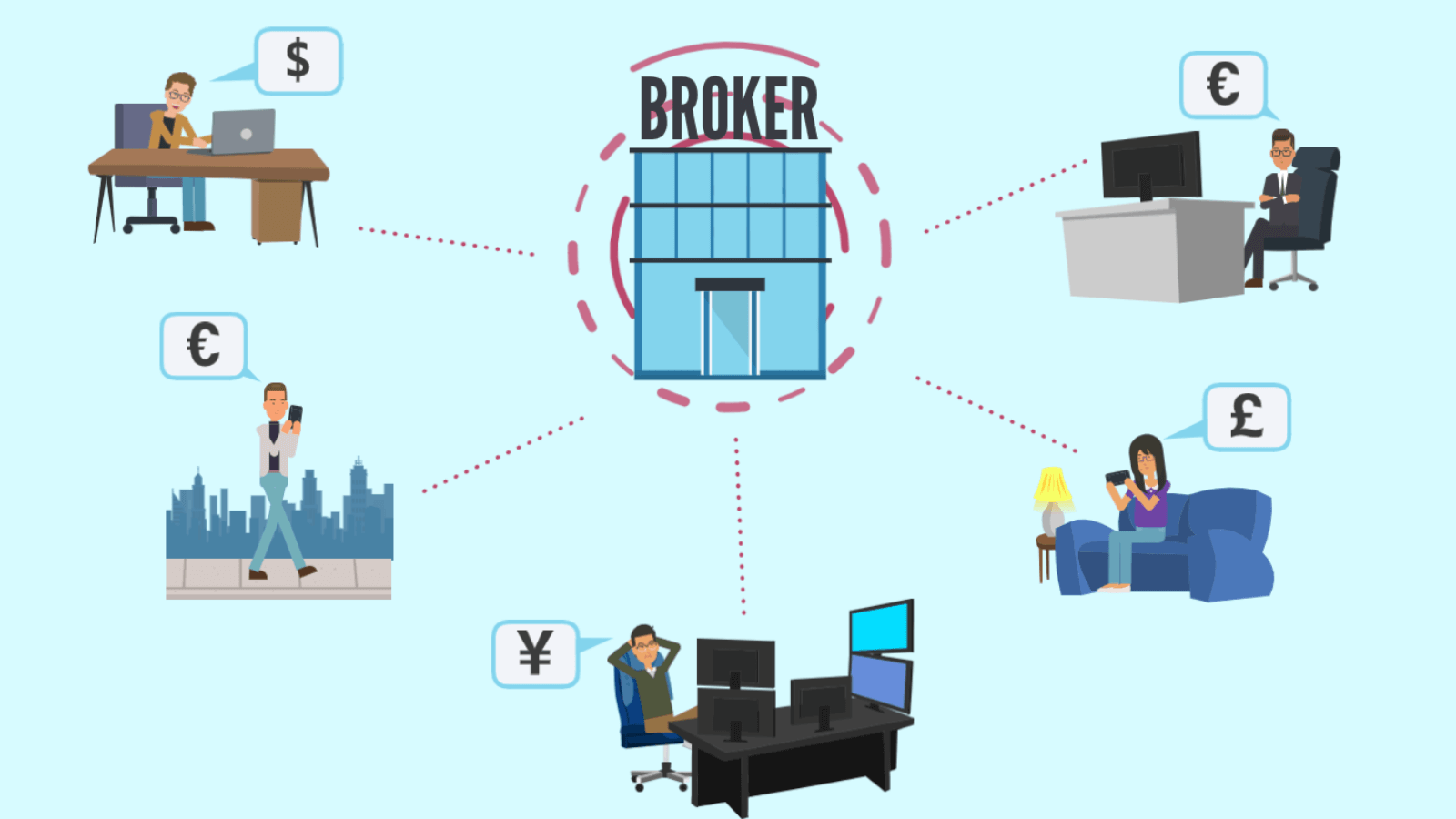
A broker or brokerage company is a place where the seller and buyer meet when trading financial assets, such as currencies.
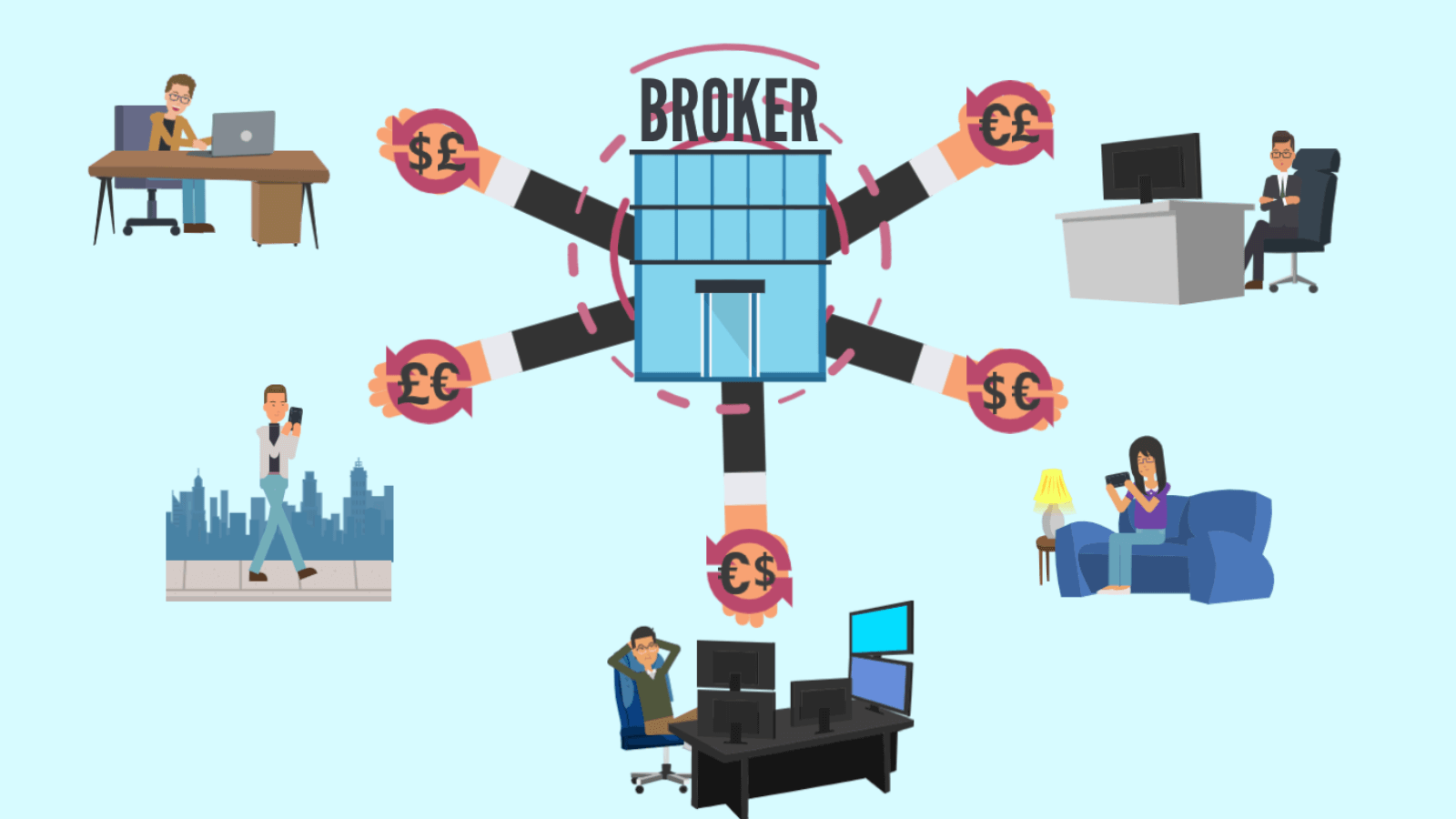
The broker acts as an intermediary between the market and the trader. That is, if you need to buy or sell an asset, the brokerage company will provide you with a seller or a buyer.
But the broker is not only an intermediary, they are also called a “liquidity provider”.
About Liquidity and its Providers
What is liquidity? Suppose you need to exchange one currency for another in a certain volume. To make this exchange, you need to find someone who is ready to sell the required currency. And to sell it, you need someone who will buy.
If there is a high demand for your currency, many people want to buy it, then there will be no problems with the sale. The same goes for buying – if there are many sellers of the currency you need, you will buy it quickly. Such a market, where there are many sellers and buyers, is called “liquid”.

There can also be another situation with market liquidity. If a person wants to buy a currency, but on the market instead of a large number of sellers (with small volumes) there are fewer sellers (large volume of currency). This also makes the market liquid. Sellers who have a lot of money are called “liquidity providers”. These providers are financial organizations or banks that trade a large amount of currency.
They trade in such volumes that the trader will most likely sell the currency to them. And the trader will also likely buy currency from them. Liquidity providers have enough funds to find buyers and sellers.
When talking about such a term as directing a contract to a liquidity provider, it is meant that the broker transfers your contract to financial organizations or banks. This means that a counterparty is sought for the transaction.
When people talk about directing a contract to a liquidity provider, they mean transferring the contract to financial organizations or banks. This means that a counterparty is sought for your transaction.
Sometimes a brokerage company is engaged in selling or buying currency without transferring transactions to liquidity providers. This means that the person is buying from the broker, not the seller. Such brokerage companies are called “market makers”.
Interaction with the Broker and Opening a Deal
Initially, brokers were interacted with by phone. That is, when you want to buy, for example, Google shares, you call your broker and give an “order” to buy. Nowadays, there is no need to call anywhere, with the help of the Internet, you can interact with the broker through special programs – trading platforms. This is much faster, simpler, and more convenient.
About Trading Platforms
A trading platform is a program that allows you to sell or buy currency. You can download the trading platform from the network and install it on your device. It helps the trader to trade currency.
There are also brokerage companies that allow transactions to be conducted in the browser. This method is more convenient because you do not need to install anything and you can trade from any device.
Differences between Brokers
At first glance, all brokerage companies look alike. But they all differ and each has its pros and cons.
The most popular types of brokers are dealing centers and companies with direct market access.
Dealing Centers or “Market Makers”
Brokers of this type act as counterparties to transactions that traders open. For example, if you buy 200 euros in such a company, the broker itself acts as the seller. At the same time, if another trader in this same company sold 200 euros, he initially sold to the broker, and then to you.
It turns out that dealing centers are a kind of “buffers” of goods, thereby providing liquidity for their traders.
Brokers with Direct Access to the Market
Such companies act as intermediaries. They receive quotes from liquidity providers (banks) and pass them on to traders. Here the counterparty is a third party.
Which Broker to Choose?
Although the type of brokerage company is an important factor in choosing, there are many other points to consider.
Regulation
Many countries have special government agencies designed to monitor the activity of financial markets in the economy. If the brokerage company is not controlled by such an agency, there is a risk that the trader will not be able to withdraw their capital.
But the fact of regulation alone is not always enough. For example, if the regulator does not have enough powers, it cannot impose sanctions on some not too conscientious brokers. And without sanctions, the laws will continue to be violated.
But also, if the regulator does not have enough powers, then traders’ money may be at risk. In case of violation of the law without sanctions, this law will not be observed. Regulators protect users and their rights.
The most competent regulatory bodies include:
- CTSC (United States); National Futures Association or NFA (United States);
- Financial Conduct Authority or FCA (UK);
- CySEC (Cyprus); BaFin (Germany);
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission or ASIC (Australia);
- JSDA (Japan);
- Financial Services Agency (Japan);
- AMF (France);
- Financial Services Authority (Malta).
Important Criteria when Choosing a Brokerage Company
At the beginning of trading, you need to decide which criteria are more important to you. Some brokerage companies offer tight spreads. This will be useful for traders who engage in short-term trading. But such companies may not provide customer service.
For other traders, it will be important to receive high-quality service, good training, for example. In this case, higher spreads may be offered, and the service may be paid additionally.
All companies talk about their merits, but the trader should choose the one that meets his requirements. You need to study all the conditions in detail and compare them with your requests.
